前言
在《单例模式学习》 中提到了,在单例对象是通过new关键字动态分配在堆上的情况下,当程序退出时,不会通过C++的RAII机制自动调用其析构函数。本文讨论一下这种现象的原因以及解决方法。
无法调用析构函数的原因
在DCLP(双检查锁模式)中,CSingleton中的instance是一个静态指针变量,被分配在全局/静态存储区。而instance所指向的CSingleton实例是通过new创建在堆上的,只能手动调用delete来释放相关资源(对于单例模式这是无法实现的,因为析构函数私有),无法通过RAII释放相关资源。
在程序结束时,instance这个指针变量被销毁了,但它所指向的内存空间中的CSingleton对象并没有被显式销毁,而是由操作系统去回收这一块内存(不会调用其析构函数)。然而依赖操作系统来清理资源并不是一个优雅的结束方式,可能会造成文件句柄未关闭、网络连接未断开等资源泄漏。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| class CSingleton
{
public:
static CSingleton* getInstance();
static std::mutex mtx;
private:
CSingleton(){}
~CSingleton(){}
CSingleton(const CSingleton&) = delete;
CSingleton& operator=(const CSingleton&) = delete;
static CSingleton* instance;
};
CSingleton* CSingleton::instance;
CSingleton* CSingleton::getInstance()
{
if(nullptr == instance)
{
mtx.lock();
if(nullptr == instance)
{
instance = new CSingleton();
}
mtx.unlock();
}
return instance;
}
|
改进方法
在讨论改进方法时,我们还是倾向于利用C++的RAII机制,而不是手动去控制释放的时机。
内嵌回收类
我们的单例类对象生命周期的开始是在第一次调用时,结束是在程序结束时。
而且我们知道①静态成员变量的生命周期是从程序启动到结束②在静态成员变量被销毁时会调用其析构函数
因此我们可以在单例类中定义一个用于释放单例类资源的内嵌类,将其析构函数定义为显式删除单例对象的操作,然后在单例类中添加一个内嵌类类型的静态成员变量garbo。
这样的话,在程序结束时garbo就会被销毁,而RAII机制确保了在销毁时会调用内嵌类CGarbo的析构函数。
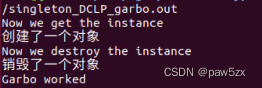
因为在~CGarbo()中delete了CSingleton::instance,所以~CSingleton()就会被调用,相关资源得以释放。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| class CSingleton
{
public:
static CSingleton* getInstance();
private:
CSingleton(){std::cout<<"创建了一个对象"<< std::endl;}
~CSingleton(){std::cout<<"销毁了一个对象"<< std::endl;}
CSingleton(const CSingleton&) = delete;
CSingleton& operator=(const CSingleton&) = delete;
static CSingleton* instance;
static std::mutex mtx;
class CGarbo
{
public:
CGarbo(){}
~CGarbo()
{
if(nullptr != CSingleton::instance)
{
delete CSingleton::instance;
instance = nullptr;
}
std::cout<<"Garbo worked"<< std::endl;
}
};
static CGarbo garbo;
};
CSingleton* CSingleton::instance;
std::mutex CSingleton::mtx;
CSingleton* CSingleton::getInstance()
{
...
}
CSingleton::CGarbo CSingleton::garbo;
|
运行结果:

智能指针
我们还可以利用智能指针引用计数机制,对资源自动管理:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
class CSingleton
{
public:
static std::shared_ptr<CSingleton> getInstance();
private:
CSingleton(){std::cout<<"创建了一个对象"<<std::endl;}
~CSingleton(){std::cout<<"销毁了一个对象"<<std::endl;}
CSingleton(const CSingleton&) = delete;
CSingleton& operator=(const CSingleton&) = delete;
static std::shared_ptr<CSingleton> instance;
static std::mutex mutex;
};
std::shared_ptr<CSingleton> CSingleton::instance;
std::mutex CSingleton::mutex;
std::shared_ptr<CSingleton> CSingleton::getInstance()
{
if (nullptr == instance)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mutex);
if (nullptr == instance)
{
instance = std::shared_ptr<CSingleton>(new CSingleton());
}
}
return instance;
}
|
注意上述代码无法通过编译,原因是当std::shared_ptr被销毁时,它会尝试使用delete来销毁管理的对象。但因为CSingleton的析构函数是私有的,所以无法从外部手动销毁CSingleton实例。
要解决这个问题,我们需要在CSingleton中自定义一个删除器,让std::shared_ptr能够调用私有析构函数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| class CSingleton
{
public:
static std::shared_ptr<CSingleton> getInstance();
private:
CSingleton(){std::cout<<"创建了一个对象"<<std::endl;}
~CSingleton(){std::cout<<"销毁了一个对象"<<std::endl;}
CSingleton(const CSingleton&) = delete;
CSingleton& operator=(const CSingleton&) = delete;
static std::shared_ptr<CSingleton> instance;
static std::mutex mutex;
static void deleter(CSingleton* p);
};
std::shared_ptr<CSingleton> CSingleton::instance;
std::mutex CSingleton::mutex;
std::shared_ptr<CSingleton> CSingleton::getInstance()
{
if (nullptr == instance)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mutex);
if (nullptr == instance)
{
instance = std::shared_ptr<CSingleton>(new CSingleton(),CSingleton::deleter);
}
}
return instance;
}
void CSingleton::deleter(CSingleton* p)
{
delete p;
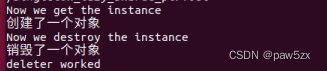
std::cout<<"deleter worked"<<std::endl;
}
|
测试结果:

局部静态变量
局部静态变量形式的单例模式也可以完成资源的释放,详见《单例模式学习》 。
1
2
3
4
5
| static CSingleton& getInstance()
{
static CSingleton instance;
return instance;
}
|